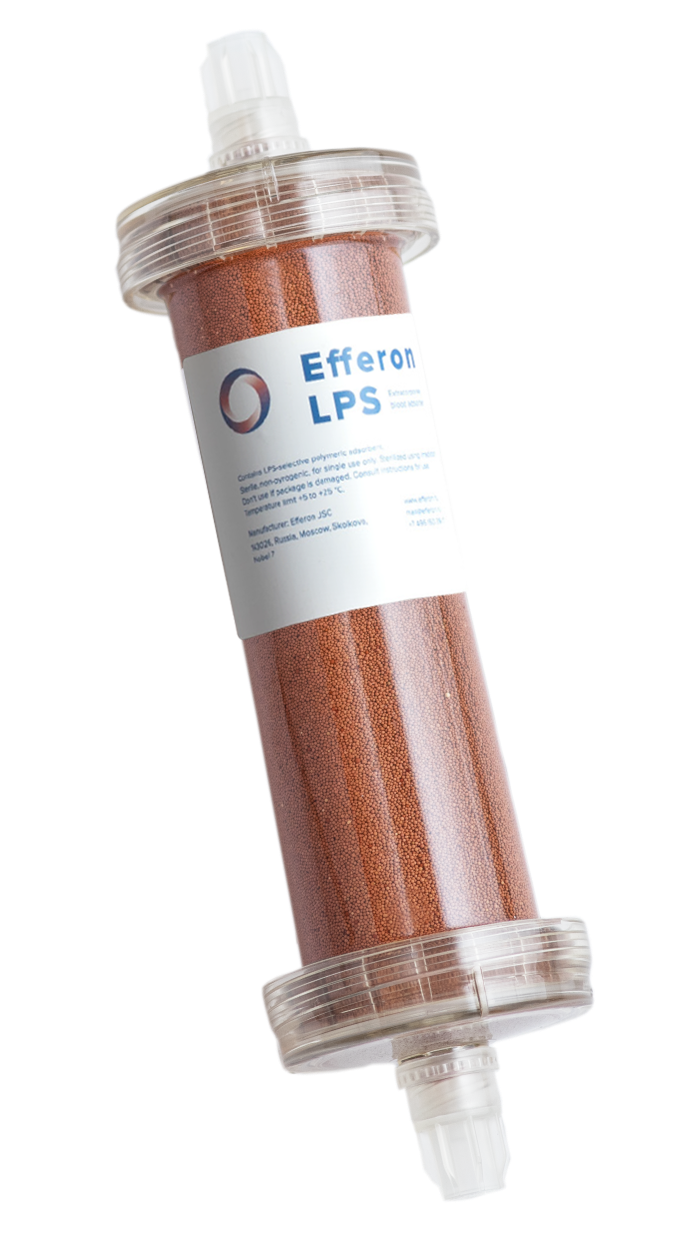
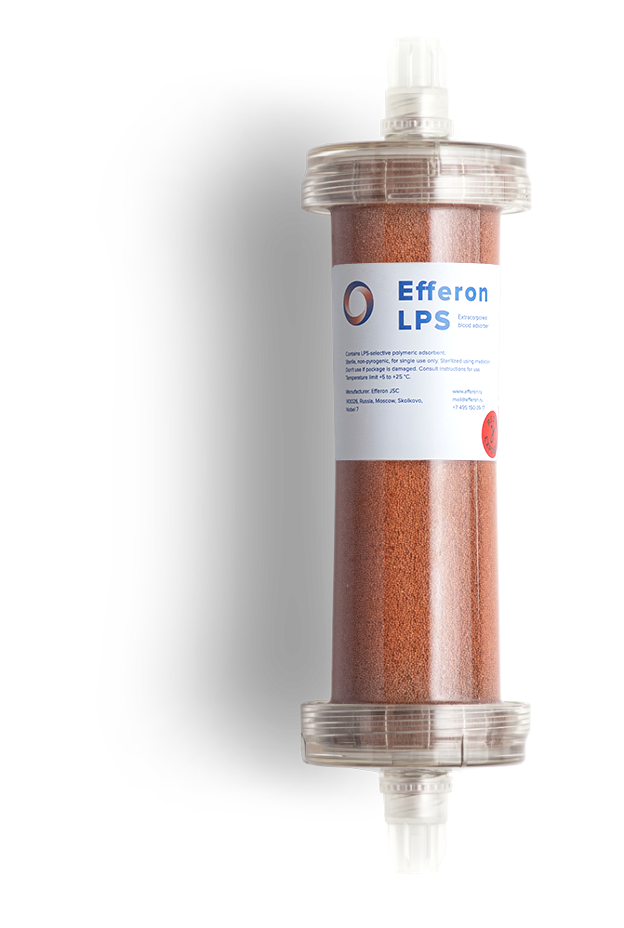
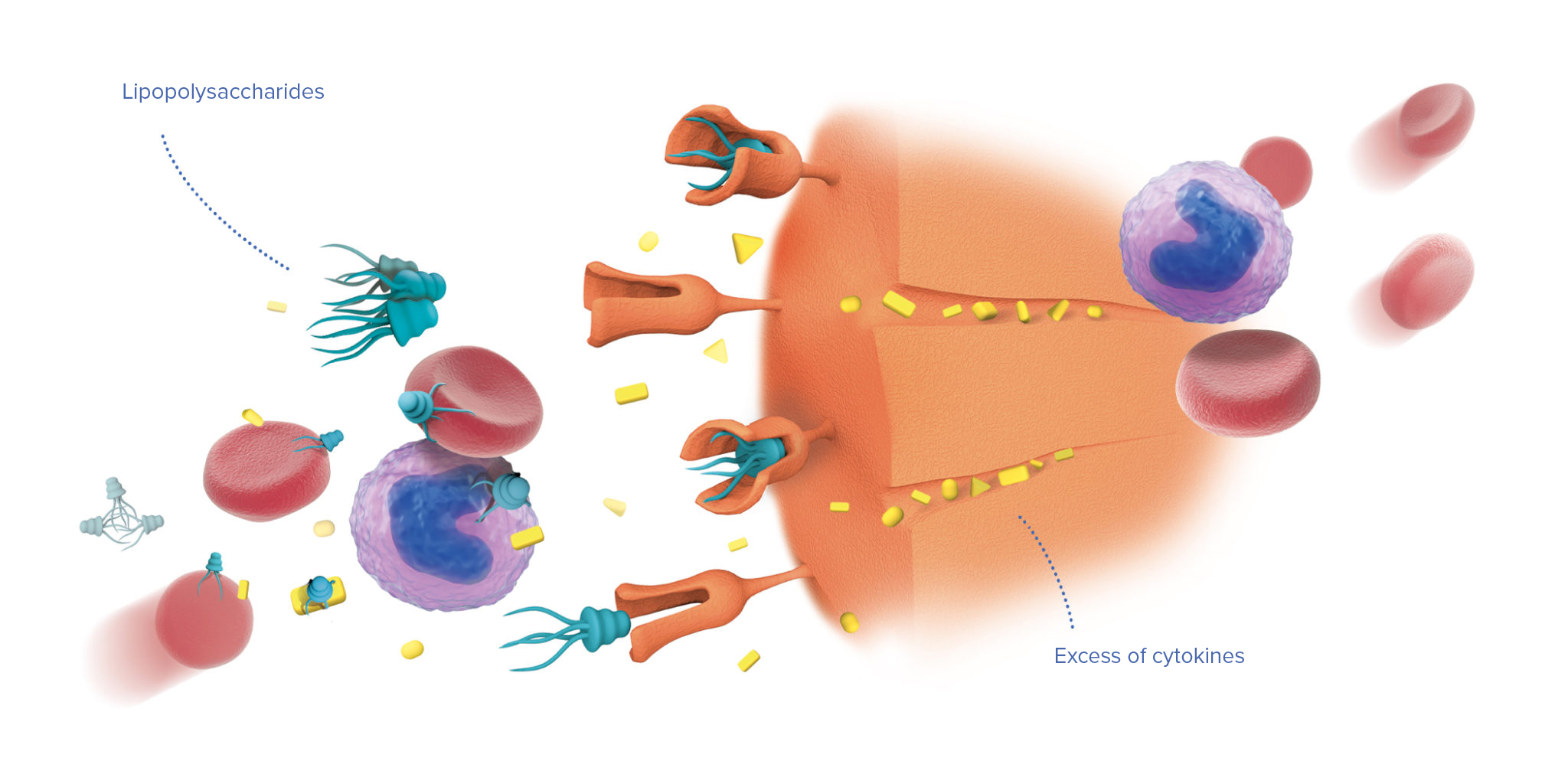
Intended use
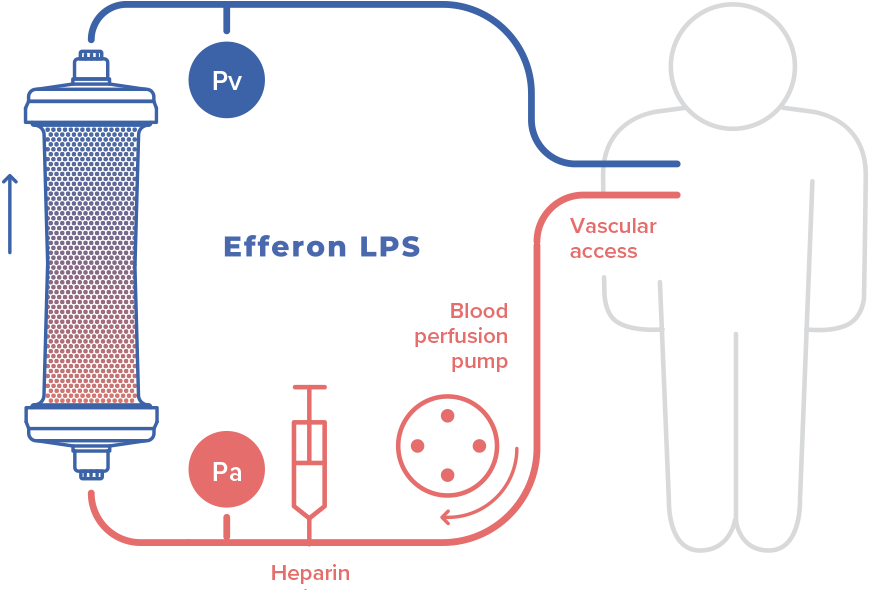
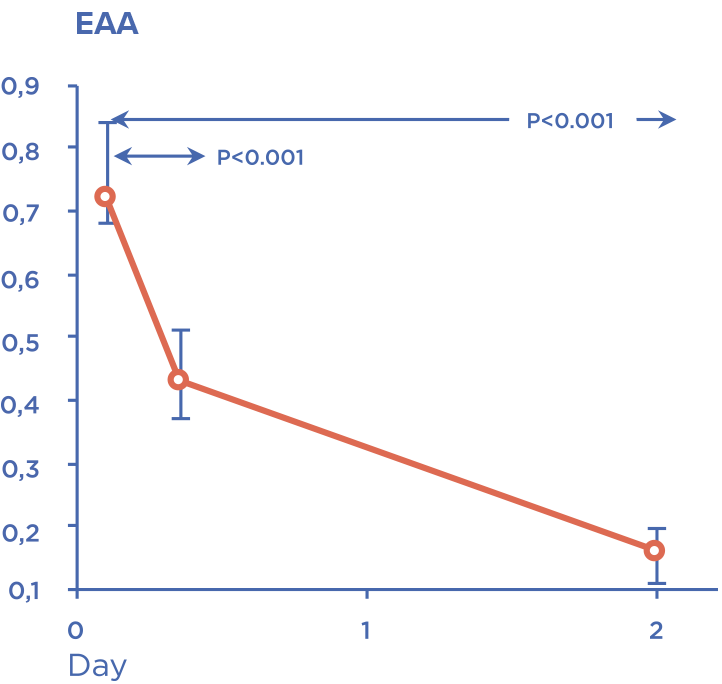
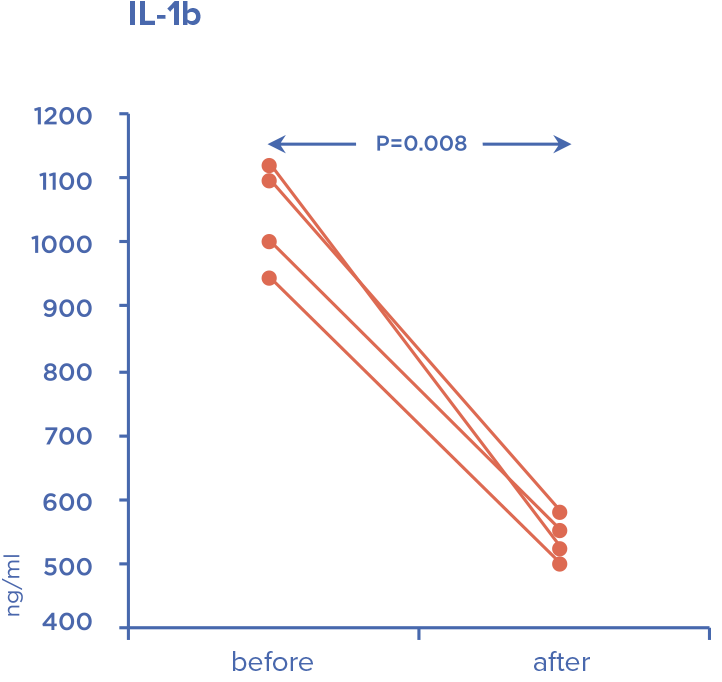
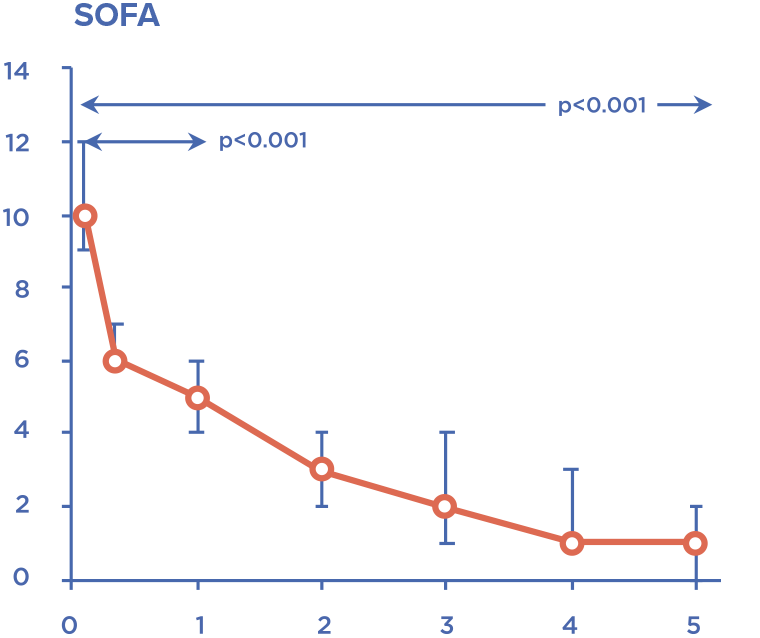
Device is intended for extracorporeal blood purification by direct hemoperfusion or in combination with hemofiltration. Detoxification is carried out by selective adsorption of lipopolysaccharides (bacterial endotoxins) and excess of endogenous inflammatory mediators.
Timely administration allows to stabilize hemodynamic parameters and prevent development of multiple organ failure.